This picture exhibits an artist’s impression of what nightglow would possibly seem like to an astronaut within the polar winter areas of Mars at evening. The inexperienced glow happens when oxygen atoms excessive up within the environment mix to type oxygen molecules.
This simulated view was created utilizing an actual however darkened picture of the Martian floor from the panoramic digicam of NASA’s Alternative rover, and an artificial nightglow equivalent to the true colour of the oxygen emission. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Cornell Univ./Arizona State Univ.– E. W. Knutsen
ESA’s ExoMars Hint Fuel Orbiter has found a inexperienced nightglow within the Martian environment, offering essential knowledge on atmospheric processes and potential illumination for future Martian missions. This phenomenon, distinct from auroras, marks a big development in our understanding of Mars.
When future astronauts discover Mars’s polar areas, they are going to see a inexperienced glow lighting up the evening sky. For the primary time, a visual nightglow has been detected within the Martian environment by ESA’s ExoMars Hint Fuel Orbiter (TGO) mission.
Below clear skies, the glow might be vibrant sufficient for people to see by and for rovers to navigate at nighttime nights. Nightglow can also be noticed on Earth. On Mars, it was one thing anticipated, but by no means noticed in seen mild till now.
Nightglow on Mars
The atmospheric nightglow happens when two oxygen atoms mix to type an oxygen molecule, about 50 km (~30 miles) above the planetary floor.
The oxygen atoms have been on a journey: they type on Mars’s dayside when daylight offers vitality to carbon dioxide molecules, making them break up aside. When the oxygen atoms migrate to the evening aspect and cease being excited by the Solar, they regroup and emit mild at decrease altitudes.
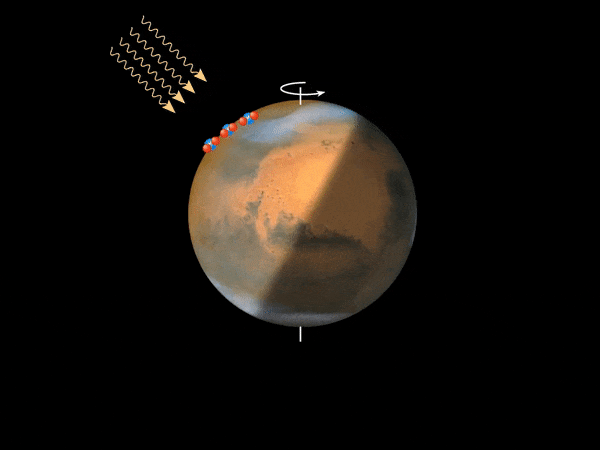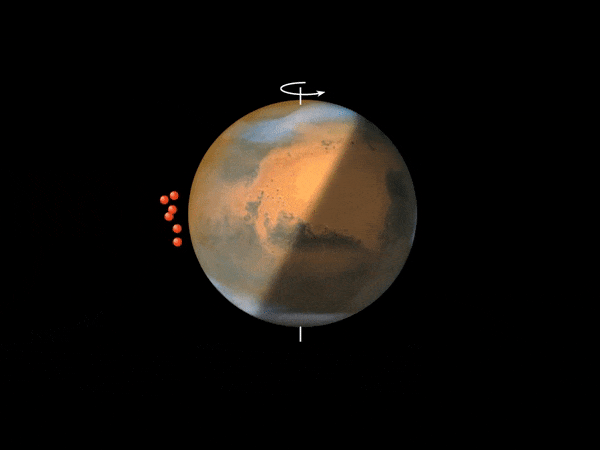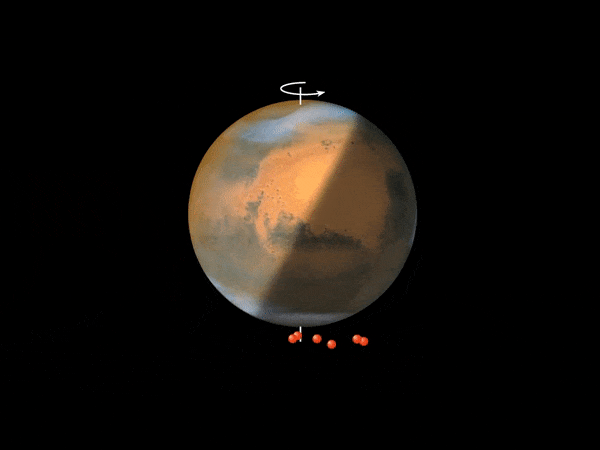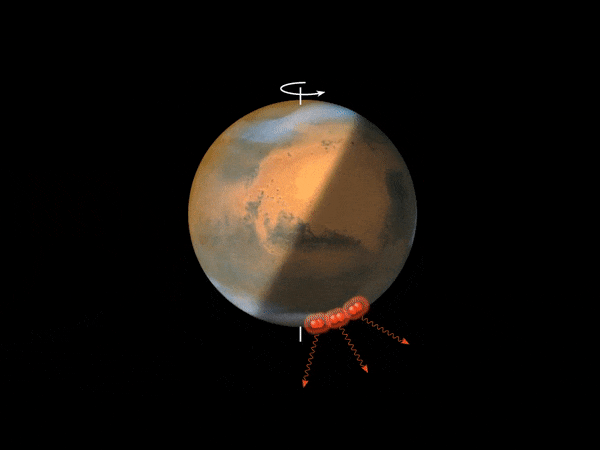
This animation depicts the method that’s believed to account for the Martian nightglow. When uncovered to photo voltaic ultraviolet radiation above an altitude of 70 km, carbon dioxide molecules – the primary atmospheric constituent of Mars’ environment – are break up into carbon monoxide and oxygen atoms. These oxygen atoms (depicted as pink spheres) are transported by a big Hadley cell, which options an ascending department above the daytime summer season pole and a descending department over the winter pole, which is within the evening hemisphere. The oxygen atoms recombine into molecular oxygen within the descending department of the Hadley cell, at an altitude of 30-50 km, emitting infrared radiation. Credit score: ESA
“This emission is because of the recombination of oxygen atoms created in the summertime environment and transported by winds to excessive winter latitudes, at altitudes of 40 to 60 km within the Martian environment,” explains Lauriane Soret, researcher from the Laboratory of Atmospheric and Planetary Physics of the College of Liège, in Belgium, and a part of the group that printed the invention in Nature Astronomy.
The illumination from the nightglow might be vibrant sufficient to mild the best way of the longer term see the glow as vibrant as moonlit clouds on Earth.
“These observations are sudden and fascinating for future journeys to the Crimson Planet,” says Jean-Claude Gérard, lead creator of the brand new examine and planetary scientist on the College of Liège.

Airglow happens in Earth’s atmospheres as daylight interacts with atoms and molecules inside the environment. On this picture, taken by astronauts aboard the Worldwide House Station (ISS) in 2011, a inexperienced band of oxygen glow is seen over Earth’s curve. On the floor, parts of northern Africa are seen, with night lights shining alongside the Nile River and its delta. Credit score: NASA
Observe the Inexperienced Glowing Highway
The worldwide scientific group was intrigued by a earlier discovery made utilizing Mars Categorical, which noticed the nightglow in infrared wavelengths a decade in the past. The Hint Fuel Orbiter adopted up by detecting glowing inexperienced oxygen atoms excessive above the dayside of Mars in 2020 – the primary time that this dayglow emission was seen round a planet aside from Earth.
These atoms additionally journey to the nightside after which recombine at decrease altitude, ensuing within the seen nightglow detected within the new analysis printed at this time.

Artist’s impression of ESA’s ExoMars Hint Fuel Orbiter detecting the inexperienced glow of oxygen within the martian environment. This emission, noticed on the dayside of Mars, is much like the evening glow seen round Earth’s environment from house. Credit score: ESA
Orbiting the Crimson Planet at an altitude of 400 km, TGO was capable of monitor the evening aspect of Mars with the ultraviolet-visible channel of its NOMAD instrument. The instrument covers a spectral vary from close to ultraviolet to pink mild and was oriented in the direction of the sting of the Crimson Planet to raised observe the higher environment.
The NOMAD experiment is led by the Royal Belgian Institute for House Aeronomy, working with groups from Spain (IAA‐CSIC), Italy (INAF‐IAPS), and the UK (Open College), amongst others.
Scientific Worth
The nightglow serves as a tracer of atmospheric processes. It could actually present a wealth of details about the composition and dynamics of a area of the environment troublesome to measure, in addition to the oxygen density. It could actually additionally reveal how vitality is deposited by each the Solar’s mild and the photo voltaic wind – the stream of charged particles emanating from our star.

Snapshot from house of the Milky Means and Earth posing collectively past the Worldwide House Station. The Milky Means stretches beneath the curve of Earth’s limb within the scene that additionally information a faint inexperienced airglow. The galaxy’s central bulge seems with starfields reduce by darkish rifts of obscuring interstellar mud. The image was taken by NASA astronaut Scott Kelly in 2015 throughout his one-year mission in house. Credit score: NASA/Scott Kelly
Understanding the properties of Mars’ environment will not be solely scientifically fascinating however it’s also key for missions to the Crimson Planet’s floor. Atmospheric density, for instance, straight impacts the drag skilled by orbiting satellites and by the parachutes used to ship probes to the Martian floor.
Nightglow Versus Aurora
Nightglow can also be noticed on Earth, however it’s not to be confused with auroras. Auroras are only one means by which planetary atmospheres mild up.
Auroras are produced, on Mars as on Earth, when energetic electrons from the Solar hit the higher environment. They range throughout house and time, whereas nightglow is extra homogeneous. Nightglow and auroras can each exhibit a variety of colours relying on which atmospheric gases are most plentiful at totally different altitudes.
The inexperienced nightglow on our planet is kind of faint, and so is greatest seen by wanting from an ‘edge on’ perspective – as portrayed in many spectacular photographs taken by astronauts from the Worldwide House Station.
A timelapse video by European House Company astronaut Tim Peake taken throughout his six-month Principia mission on the Worldwide House Station. The British astronaut commented on this timelapse: “Worldwide House Station view of an ‘aurora rise’ – spot the 2 satellites on the finish? Timelapse video constructed from photographs taken at one second intervals performed again 25 instances sooner.” Credit score: ESA/NASA
Reference: “Statement of the Mars O2 seen nightglow by the NOMAD spectrometer onboard the Hint Fuel Orbiter” by J.-C. Gérard, L. Soret, I. R. Thomas, B. Ristic, Y. Willame, C. Depiesse, A. C. Vandaele, F. Daerden, B. Hubert, J. P. Mason, M. R. Patel and M. A. López-Valverde, 9 November 2023, Nature Astronomy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41550-023-02104-8
